Understanding and Overcoming Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction is a pervasive and life-altering condition, characterized by the compulsive use of opioids despite harmful consequences. Opioids, which include prescription pain relievers (such as oxycodone and hydrocodone), heroin, and synthetic opioids like fentanyl, act on the nervous system to provide pain relief and a sense of euphoria. While they are effective for managing pain, their high potential for misuse and addiction has created a widespread crisis.
The Scope and Impact of Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction affects individuals and families across all demographics, with devastating physical, emotional, and societal consequences. Over time, continued opioid use can lead to tolerance, where larger doses are required to achieve the same effect, as well as dependence. Once dependence develops, stopping use can result in withdrawal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, sweating, anxiety, muscle pain, and cravings, which often make it difficult to quit without professional help.
The risks associated with opioid addiction extend beyond dependency. The potential for overdose, particularly with powerful synthetic opioids like fentanyl, is alarmingly high. Overdoses can lead to respiratory failure, brain damage, or death, making prompt treatment and intervention critical.
For families, the impact of opioid addiction can be deeply emotional. Loved ones may feel powerless as they watch someone they care about struggle with dependency, but it’s important to know that help is available, and recovery is possible.
Treatment Options for Opioid Addiction
Effective treatment requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the physical, psychological, and emotional aspects of dependency. Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) is one of the most effective tools for managing withdrawal symptoms and reducing cravings. Medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone can stabilize individuals in recovery and lower the risk of relapse.
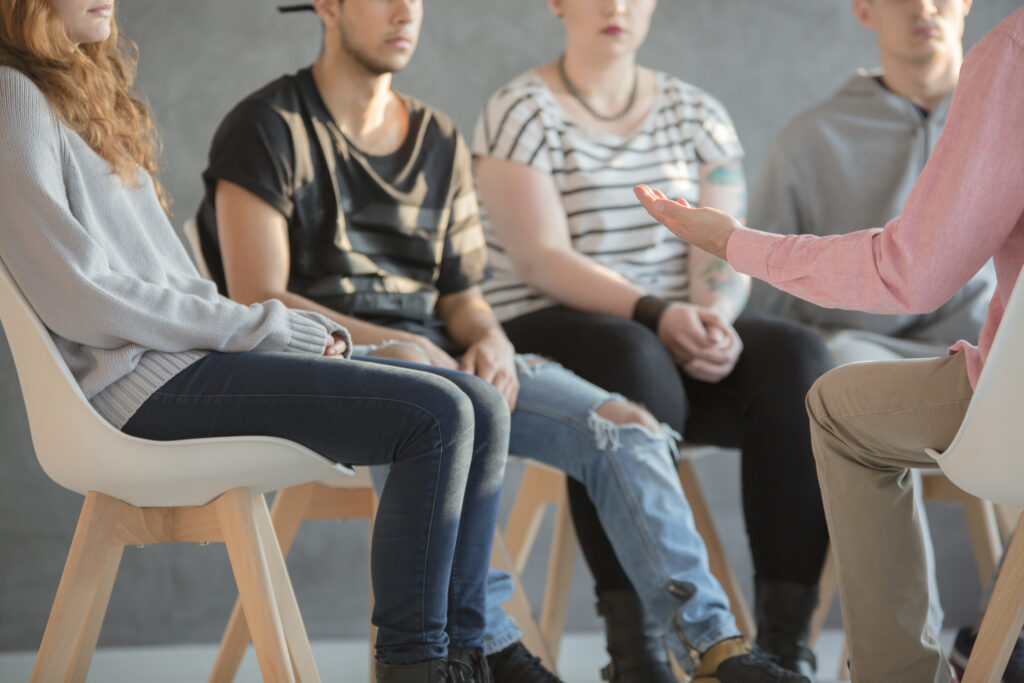
Counselling and therapy are essential components of opioid addiction treatment. Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) helps individuals understand and address the triggers that lead to substance use, while family therapy can repair relationships and rebuild trust. Support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous (NA), also play a critical role in recovery by providing a sense of community and accountability.

Addressing Different Forms of Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction encompasses a wide range of substances, each presenting unique challenges. Prescription opioids, such as oxycodone, morphine, and hydrocodone, may be misused after being prescribed for legitimate medical needs. Heroin, a street drug derived from morphine, is often used as a cheaper alternative to prescription opioids, while synthetic opioids like fentanyl are particularly potent and dangerous, even in small amounts. Treatment plans are tailored to the specific substance and circumstances of each individual to provide the best chance of recovery.
Support for Individuals and Families
Recovery is a journey that requires compassion, dedication, and the right support system. For individuals, taking the first step toward treatment can feel overwhelming, but professional guidance can make all the difference. Families can also play a vital role in the recovery process by offering encouragement and seeking help for their loved ones.
If you or someone you care about is struggling with opioid addiction, don’t wait to seek help. Contact one of our Addiction Experts today. Together, we can explore treatment options and start building a healthier, substance-free future.
Search
Find the best match of your interest